Penilaian Kerentanan Bangunan Terhadap Gempa Bumi pada Gedung Perkuliahan Berlantai Tinggi di Yogyakarta
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18196/bce.v1i2.11075Keywords:
Kerentanan, Gempa Bumi, Rapid Visual Screening, Gedung Perkuliahan, FEMA P-154Abstract
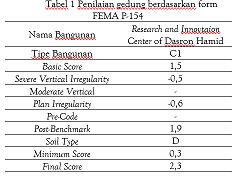
Yogyakarta, an area that has a high level of risk for earthquakes, can result into potential damage to the buildings erected it. The earthquake that occurred on May 27 th 2006 still leaving a trauma, according to BNPB (2012) the yogyakarta quake caused 4.674 people die and 19.897 others had seriously injuries. Most victims were caused by the falling building and materials. This disaster caused heavy damage to buildings at 96.790, with 117.075 moderate damage, and as well as 156.971. The construction of the new building in Yogyakarta is expected to be able to apply the principles of the earthquake resistant building to minimize the impact of it. Dasron Hamid Research and Innovation Center is the one of building which currently under construction that apply the principles. This research aim to determine the level of vulnerability of RIC buildings to earthquakes using RVS (Rapid Visual Screening) based on FEMA P-154 2015. It was carried out by quantitative methods and direct observation at the construction site by filling in the FEMA P-154 form, this building is consist of 8 floor with 1 ground floor. The form that used is a high seismic type, which means the level of seismicity in the research location has a high earthquake spread. Based on the research, was got result obtain value of 2,3 with the vulnerability of the building to collapse is 0,5%, so the building is safe against earthquakes. This is because the building is erected after a reference or code exists even though it has irregularities such as vertical irregularity and, plan irregularity.
References
Aritonang, T.S.M., Satyarno, I., dan Supriyadi, B., 2011, Perfomance Evaluation Of The IRD RSUP Dr. Sardjito Building To The Influence Of Earthquake, Civil Engginering Forum. 20(1), 1183-1188.
Badan Nasional Penanggulangan Bencana (BNPB), 2012, Peraturan Kepala BNPB Nomor 2 Tahun 2012 tentang Pedoman Umum Pengkajian Risiko Bencana, Jakarta.
Bawono, A. S. (2016). Studi Kerentanan Bangunan Akibat Gempa: Studi Kasus Perumahan Di Bantul. Semesta Teknika, 19(1), 90-97.
Devi, K., & Naroem, N. (2015). Seismic Vulnerability Assessment of Excisting Buildings: It’s Importance. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring (IJITEE), 4(9), 39-46.
Faizah, R., & Syamsi, M. I. (2017). Asesmen Cepat Kerentanan Bangunan Sekolah Muhammadiyah Terhadap Gempabumi di Kecamatan Kasihan Bantul DIY. Semesta Teknika, 20(2), 164-171.
FEMA 154, 2015, Rapid Visual Screening of Buildings for Potensial Seismic Hazards : A Handbook, Third Edition. Federal Emergency Management Agency, USA.
Ghafar. M., Ramly, N., Alel. M., Adnan, A., Mohamad., E.T., dan Yunus. M.Z.M., 2015, A Simplified Method for Preliminary Seismic Vulnerability Assessment of Existing Building in Kundasang, Sabah, Malaysia, Jurnal Teknologi, 72(3), 1-7
Shivkant, M.S., 2017, Rapid Visual Screening of Buildings for Potential Seismic Hazards: A Case Study of Chiplun City, International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), 4(7), 2419-2423.
Srikanth, T., Kumar, R.P., Singh, A.P., Rastogi, B.K., dan Kumar, S., 2010, Earthquake Vulnerability Assessment of Existing Buildings in Gandhidham and Adipur Cities Kachchh, Gujarat (India), European Journal of Scientific Research, 41(3), 336-353.
Zulfiar, M. H. (2018). Pemeriksaan Material pada Pembangunan Rumah Non-Engineered di Daerah Rawan Gempa Dusun Serut, Palbapang Kabupaten Bantul, Yogyakarta. Semesta Teknika, 21(2), 178-188.
Zulfiar, M. H., & Jayady, A. (2018). Kajian Kerentanan Pada Sektor Konstruksi Dalam Pengurangan Risiko Bencana Gempa Bumi. Jurnal Karkasa, 4(1), 21-27.
Zulfiar, M. H., Jayady, A., Saputra, J., & Rukmono, N. (2018). Kerentanan Bangunan Rumah Cagar Budaya Terhadap Gempa di Yogyakarta. Jurnal Karkasa, 4(1), 5-12.
Zulfiar, M. H., Tamin, T., Pribadi, K. S., & Irwan, I. (2014). Identifikasi Faktor Dominan Penyebab Kerentanan Bangunan Di Daerah Rawan Gempa, Provinsi Sumatera Barat. Semesta Teknika, 17(2), 116-125.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright
The Authors submitting a manuscript do so on the understanding that if accepted for publication, copyright of the article shall be assigned to Bulletin of Civil Engineering (BCE). Copyright encompasses rights to reproduce and deliver the article in all form and media, including reprints, photographs, microfilms, and any other similar reproductions, as well as translations.
Authors should sign Copyright Transfer Agreement when they have approved the final proofs sent by the journal prior the publication. BCE strives to ensure that no errors occur in the articles that have been published, both data errors and statements in the article.
BCE keep the rights to articles that have been published and hold the copyright limited solely for the publication. Authors are permitted to disseminate published article by sharing the link of BCE website. Authors are allowed to use their works for any purposes deemed necessary without written permission from BCE with an acknowledgement of initial publication in this journal.
License
All articles published in BCE are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-SA) license. You are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms. Under the following terms:
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- ShareAlike — If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same license as the original.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.


